Storage Cluster Quick Start¶
If you haven’t completed your Preflight Checklist, do that first. This
Quick Start sets up a Ceph Storage Cluster using ceph-deploy
on your admin node. Create a three Ceph Node cluster so you can
explore Ceph functionality.
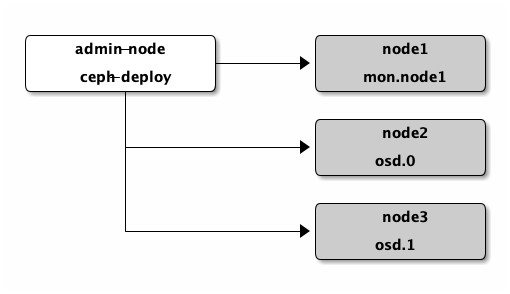
As a first exercise, create a Ceph Storage Cluster with one Ceph Monitor and two
Ceph OSD Daemons. Once the cluster reaches a active + clean state, expand it
by adding a third Ceph OSD Daemon, a Metadata Server and two more Ceph Monitors.
For best results, create a directory on your admin node node for maintaining the
configuration files and keys that ceph-deploy generates for your cluster.
mkdir my-cluster
cd my-cluster
The ceph-deploy utility will output files to the current directory. Ensure you
are in this directory when executing ceph-deploy.
Important
Do not call ceph-deploy with sudo or run it as root
if you are logged in as a different user, because it will not issue sudo
commands needed on the remote host.
Disable requiretty
On some distributions (e.g., CentOS), you may receive an error while trying
to execute ceph-deploy commands. If requiretty is set
by default, disable it by executing sudo visudo and locate the
Defaults requiretty setting. Change it to Defaults:ceph !requiretty to
ensure that ceph-deploy can connect using the ceph user and execute
commands with sudo.
Create a Cluster¶
If at any point you run into trouble and you want to start over, execute the following to purge the configuration:
ceph-deploy purgedata {ceph-node} [{ceph-node}]
ceph-deploy forgetkeys
To purge the Ceph packages too, you may also execute:
ceph-deploy purge {ceph-node} [{ceph-node}]
If you execute purge, you must re-install Ceph.
On your admin node from the directory you created for holding your
configuration details, perform the following steps using ceph-deploy.
Create the cluster.
ceph-deploy new {initial-monitor-node(s)}
For example:
ceph-deploy new node1
Check the output of
ceph-deploywithlsandcatin the current directory. You should see a Ceph configuration file, a monitor secret keyring, and a log file for the new cluster. See ceph-deploy new -h for additional details.Change the default number of replicas in the Ceph configuration file from
3to2so that Ceph can achieve anactive + cleanstate with just two Ceph OSDs. Add the following line under the[global]section:osd pool default size = 2
If you have more than one network interface, add the
public networksetting under the[global]section of your Ceph configuration file. See the Network Configuration Reference for details.public network = {ip-address}/{netmask}
Install Ceph.
ceph-deploy install {ceph-node}[{ceph-node} ...]
For example:
ceph-deploy install admin-node node1 node2 node3
The
ceph-deployutility will install Ceph on each node. NOTE: If you useceph-deploy purge, you must re-execute this step to re-install Ceph.Add the initial monitor(s) and gather the keys:
ceph-deploy mon create-initial
Once you complete the process, your local directory should have the following keyrings:
{cluster-name}.client.admin.keyring{cluster-name}.bootstrap-osd.keyring{cluster-name}.bootstrap-mds.keyring{cluster-name}.bootstrap-rgw.keyring
Note
The bootstrap-rgw keyring is only created during installation of clusters running Hammer or newer
Add two OSDs. For fast setup, this quick start uses a directory rather than an entire disk per Ceph OSD Daemon. See ceph-deploy osd for details on using separate disks/partitions for OSDs and journals. Login to the Ceph Nodes and create a directory for the Ceph OSD Daemon.
ssh node2 sudo mkdir /var/local/osd0 exit ssh node3 sudo mkdir /var/local/osd1 exit
Then, from your admin node, use
ceph-deployto prepare the OSDs.ceph-deploy osd prepare {ceph-node}:/path/to/directory
For example:
ceph-deploy osd prepare node2:/var/local/osd0 node3:/var/local/osd1
Finally, activate the OSDs.
ceph-deploy osd activate {ceph-node}:/path/to/directory
For example:
ceph-deploy osd activate node2:/var/local/osd0 node3:/var/local/osd1
Use
ceph-deployto copy the configuration file and admin key to your admin node and your Ceph Nodes so that you can use thecephCLI without having to specify the monitor address andceph.client.admin.keyringeach time you execute a command.ceph-deploy admin {admin-node} {ceph-node}
For example:
ceph-deploy admin admin-node node1 node2 node3
When
ceph-deployis talking to the local admin host (admin-node), it must be reachable by its hostname. If necessary, modify/etc/hoststo add the name of the admin host.Ensure that you have the correct permissions for the
ceph.client.admin.keyring.sudo chmod +r /etc/ceph/ceph.client.admin.keyring
Check your cluster’s health.
ceph health
Your cluster should return an
active + cleanstate when it has finished peering.
Operating Your Cluster¶
Deploying a Ceph cluster with ceph-deploy automatically starts the cluster.
To operate the cluster daemons with Debian/Ubuntu distributions, see
Running Ceph with Upstart. To operate the cluster daemons with CentOS,
Red Hat, Fedora, and SLES distributions, see Running Ceph with sysvinit.
To learn more about peering and cluster health, see Monitoring a Cluster. To learn more about Ceph OSD Daemon and placement group health, see Monitoring OSDs and PGs. To learn more about managing users, see User Management.
Once you deploy a Ceph cluster, you can try out some of the administration
functionality, the rados object store command line, and then proceed to
Quick Start guides for Ceph Block Device, Ceph Filesystem, and the Ceph Object
Gateway.
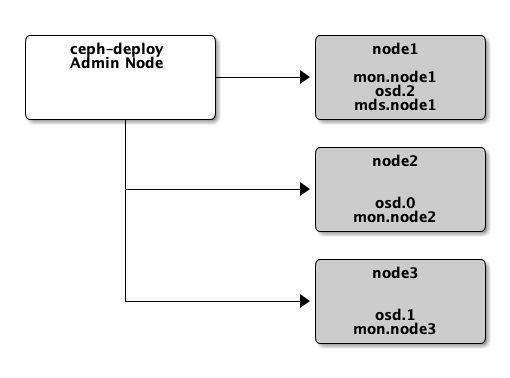
Expanding Your Cluster¶
Once you have a basic cluster up and running, the next step is to expand
cluster. Add a Ceph OSD Daemon and a Ceph Metadata Server to node1.
Then add a Ceph Monitor to node2 and node3 to establish a
quorum of Ceph Monitors.
Adding an OSD¶
Since you are running a 3-node cluster for demonstration purposes, add the OSD to the monitor node.
ssh node1
sudo mkdir /var/local/osd2
exit
Then, from your ceph-deploy node, prepare the OSD.
ceph-deploy osd prepare {ceph-node}:/path/to/directory
For example:
ceph-deploy osd prepare node1:/var/local/osd2
Finally, activate the OSDs.
ceph-deploy osd activate {ceph-node}:/path/to/directory
For example:
ceph-deploy osd activate node1:/var/local/osd2
Once you have added your new OSD, Ceph will begin rebalancing the cluster by
migrating placement groups to your new OSD. You can observe this process with
the ceph CLI.
ceph -w
You should see the placement group states change from active+clean to active
with some degraded objects, and finally active+clean when migration
completes. (Control-c to exit.)
Add a Metadata Server¶
To use CephFS, you need at least one metadata server. Execute the following to create a metadata server:
ceph-deploy mds create {ceph-node}
For example:
ceph-deploy mds create node1
Note
Currently Ceph runs in production with one metadata server only. You may use more, but there is currently no commercial support for a cluster with multiple metadata servers.
Add an RGW Instance¶
To use the Ceph Object Gateway component of Ceph, you must deploy an instance of RGW. Execute the following to create an new instance of RGW:
ceph-deploy rgw create {gateway-node}
For example:
ceph-deploy rgw create node1
Note
This functionality is new with the Hammer release, and also with
ceph-deploy v1.5.23.
By default, the RGW instance will listen on port 7480. This can be changed by editing ceph.conf on the node running the RGW as follows:
[client]
rgw frontends = civetweb port=80
To use an IPv6 address, use:
[client]
rgw frontends = civetweb port=[::]:80
Adding Monitors¶
A Ceph Storage Cluster requires at least one Ceph Monitor to run. For high availability, Ceph Storage Clusters typically run multiple Ceph Monitors so that the failure of a single Ceph Monitor will not bring down the Ceph Storage Cluster. Ceph uses the Paxos algorithm, which requires a majority of monitors (i.e., 1, 2:3, 3:4, 3:5, 4:6, etc.) to form a quorum.
Add two Ceph Monitors to your cluster.
ceph-deploy mon add {ceph-node}
For example:
ceph-deploy mon add node2 node3
Once you have added your new Ceph Monitors, Ceph will begin synchronizing the monitors and form a quorum. You can check the quorum status by executing the following:
ceph quorum_status --format json-pretty
Tip
When you run Ceph with multiple monitors, you SHOULD install and configure NTP on each monitor host. Ensure that the monitors are NTP peers.
Storing/Retrieving Object Data¶
To store object data in the Ceph Storage Cluster, a Ceph client must:
Set an object name
Specify a pool
The Ceph Client retrieves the latest cluster map and the CRUSH algorithm calculates how to map the object to a placement group, and then calculates how to assign the placement group to a Ceph OSD Daemon dynamically. To find the object location, all you need is the object name and the pool name. For example:
ceph osd map {poolname} {object-name}
Exercise: Locate an Object
As an exercise, lets create an object. Specify an object name, a path to
a test file containing some object data and a pool name using the
rados put command on the command line. For example:
echo {Test-data} > testfile.txt
rados put {object-name} {file-path} --pool=data
rados put test-object-1 testfile.txt --pool=data
To verify that the Ceph Storage Cluster stored the object, execute the following:
rados -p data ls
Now, identify the object location:
ceph osd map {pool-name} {object-name}
ceph osd map data test-object-1
Ceph should output the object’s location. For example:
osdmap e537 pool 'data' (0) object 'test-object-1' -> pg 0.d1743484 (0.4) -> up [1,0] acting [1,0]
To remove the test object, simply delete it using the rados rm
command. For example:
rados rm test-object-1 --pool=data
As the cluster evolves, the object location may change dynamically. One benefit of Ceph’s dynamic rebalancing is that Ceph relieves you from having to perform the migration manually.
